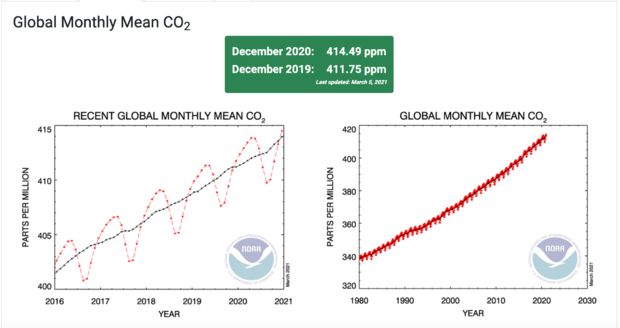
Levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane in the atmosphere continued to rise in 2020, with CO2 levels reaching its highest point in 3.6 million years, according to calculations by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The barrier was broken despite a reduction in expected emissions from the COVID-19 pandemic
NOAA reported that the global average of atmospheric CO2 reached 412.5 parts per million (ppm) in 2020, an increase of 2.6 ppm from 2019, the fifth largest increase since they started measuring atmospheric CO2 levels. The increase happened despite an estimated 7% reduction in global emissions from the pandemic. Pieter Tans, the senior scientist at NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory, estimates that 2020 would have been a record year had it not been for the pandemic.
Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego published similar findings on Wednesday, saying their measurements showed atmospheric CO2 levels were 417.4 ppm at their Hawaii monitoring station. Scripps noted that this puts atmospheric CO2 levels 50% higher than just before the industrial revolution.
Scripps also noted that the amount of CO2 that accumulates in the atmosphere is accelerating. “It has taken more than 200 years for levels to rise by 25%, but now just over 30 years later, levels have risen by 50%,” the institution said. Should current trends continue, it predicts that CO2 levels will be twice the pre-industrial levels in about 55 years.
NOAA
CO2 is considered a greenhouse gas due to its ability to retain heat. According to a recent NASA study, greenhouse gases and particulate matter in the atmosphere caused by the combustion of fossil fuels are responsible for most of the warming that has been documented over the past century.
According to NOAA, the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere is now comparable to a time when the Earth was about 7 degrees warmer than in the United States pre-industrial time period and sea level were nearly 25 meters higher than they are today.
NOAA also found that levels of methane, another greenhouse gas, increased dramatically in 2020. “NOAA’s preliminary analysis showed that the annual increase in atmospheric methane for 2020 was 14.7 parts per billion (ppb), which is the largest annual increase. since the beginning of systematic measurements in 1983, ”the government said.
NOAA noted that, as is usually the case, this report is preliminary and the final calculation of greenhouse gas levels is usually slightly lower than preliminary figures. It said that, even with the latest calculations, “the rise in 2020 is likely to remain one of the largest in the entire record.”